Introduction
After applying a discount rate that accounts for the risk of preferred stock and the opportunity cost of capital, the value of a preferred stock is equal to the present value (PV) of the preferred stock's regular dividends (i.e., the cash flows paid to preferred shareholders). The purchase price of a company's preferred stock is the cash it receives in exchange for the profits it makes from the stock's issuance and sale. It's calculated by dividing the annualized profit from stock sales by the total profit the company saw from stock sales. The preferred stock price is calculated annually by dividing the preferred dividend by the stock's closing price. Once they have that rate, they can evaluate it alongside other financing options. The preferred share price can also be factored into the WACC formula.
What is Startup Preferred Stock?
Equity, or stock in the company, is one of a startup's most valuable assets. Startups offering stock options are more likely to attract top employees and early-stage investors. It's common for a startup to offer both preferred and common stock to its investors. It's a stake in the business that typically comes with voting privileges. Even though both common stock and preferred stock are types of ownership, common stock has voting rights, and the preferred stock does not.
Formula
To calculate the worth of typically preferred stock, use the following formula.
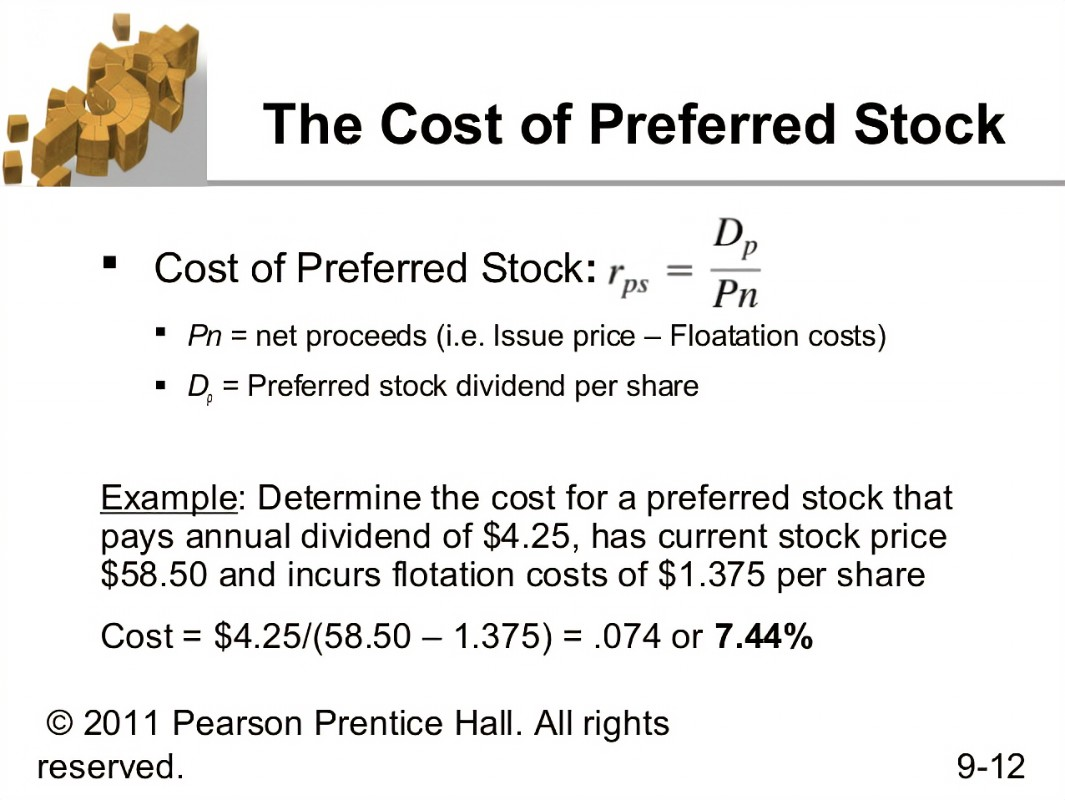
V.P. = DP/kp = P x dp/kp
Price of dividend (future stream of income) per share of preferred stock/dividend payout ratio (required yield). The symbol VP denotes the value of the preferred stock in this context. Preferred stockholders receive a yearly dividend payment, denoted by the DP. The rate of return, or KP, is the Price per share of preferred stock is denoted by its par value, while the preferred dividend yield is denoted by dp.
The DP is calculated by multiplying the stock's par value (also called the face value) by the dividend per share payout ratio. The required rate of return reflects how the market values the risks associated with the preferred stock in question. Preferred stock dividends are paid on a fixed schedule but are paid indefinitely because the stock itself will never expire. If preferred stock dividends grow at a constant rate of g, the stock's value will equal that of a rising perpetually at any given time. Preferred stock with embedded options, such as the ability to be converted or called, will have a different price.
Unique Features of Preferred Shares
The preferred stock differs from common stock because the holders prioritise claiming company assets. This makes them the first to receive funds in the event of bankruptcy, ahead of regular shareholders. Also, like bondholders, preferred stockholders are entitled to the same fixed dividend from the company. The preferred share's valuation is based on the dividend, which may be paid monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the company's policy. Dividends are typically established as either a fixed dollar amount or a percentage of the share price. It's the kind of money that comes in regularly and never stops.
What is the Difference Between Common Stock and Preferred Stock?
A shareholder in the company who owns common stock has gained control of the business and voting privileges. This gives them a say in matters such as who serves on the board of directors and how the company is managed. The larger your stake in the company, the more weight your vote carries. Preference shares Contrarily, there are benefits associated with compared to regular stock. Key differences between preferred and common stock are as follows: Both common and preferred stockholders are initially equal owners of a company, but only common stockholders are granted voting rights.
Nuances to the Cost of Preferred Stock
The yield and the financing cost can be impacted by any special features issued with the preferred stock.Preferred stock features may include call options, conversion to common stock, cumulative pay-in-kind dividends, and more. Due to the high degree of uncertainty inherent in estimating the Price for the preferred stock, there is no established procedure for dealing with such situations.
You'll have to make whatever adjustments you think are necessary based on the highest likely outcome, which is highly subjective. For instance, in the case of preferred equity with convertible options, the security may be split into separate equity (straight-debt treatment) and equity (conversion option) components based on the most likely outcome.
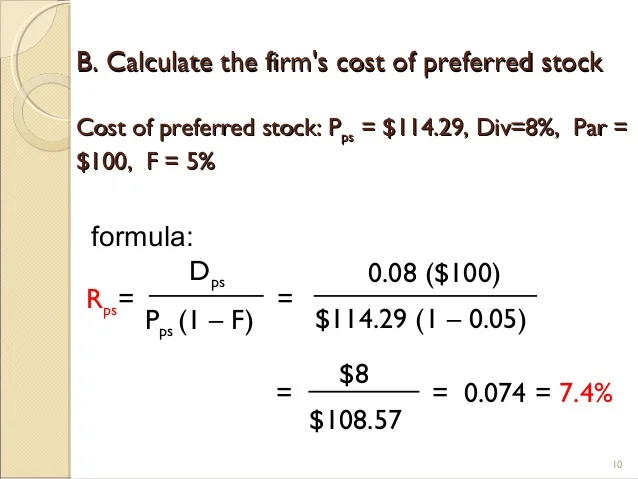
Conclusion:
They are equity securities in the strictest sense. They pay dividends consistently but lack voting rights, similar to debt instruments. In the event of bankruptcy or liquidation, preferred shareholders have priority over common shareholders and are entitled to a larger dividend payout. That's why it's important to use models like dividend growth when valuing preferred stock.